We live in a world where data is the new oil which makes protecting personal information paramount for businesses of all sizes. Data privacy is the cornerstone of customer trust and corporate reputation. With the rapid digitization of services and the ever-increasing amount of data being generated, ensuring robust data privacy and security measures is essential.
As an entrepreneur, actively prioritising privacy, security and trust for all stakeholders in the business is something I highly value. Keep reading as I talk in detail about the importance of data privacy in business, key compliance regulations and effective security strategies to protect sensitive information.
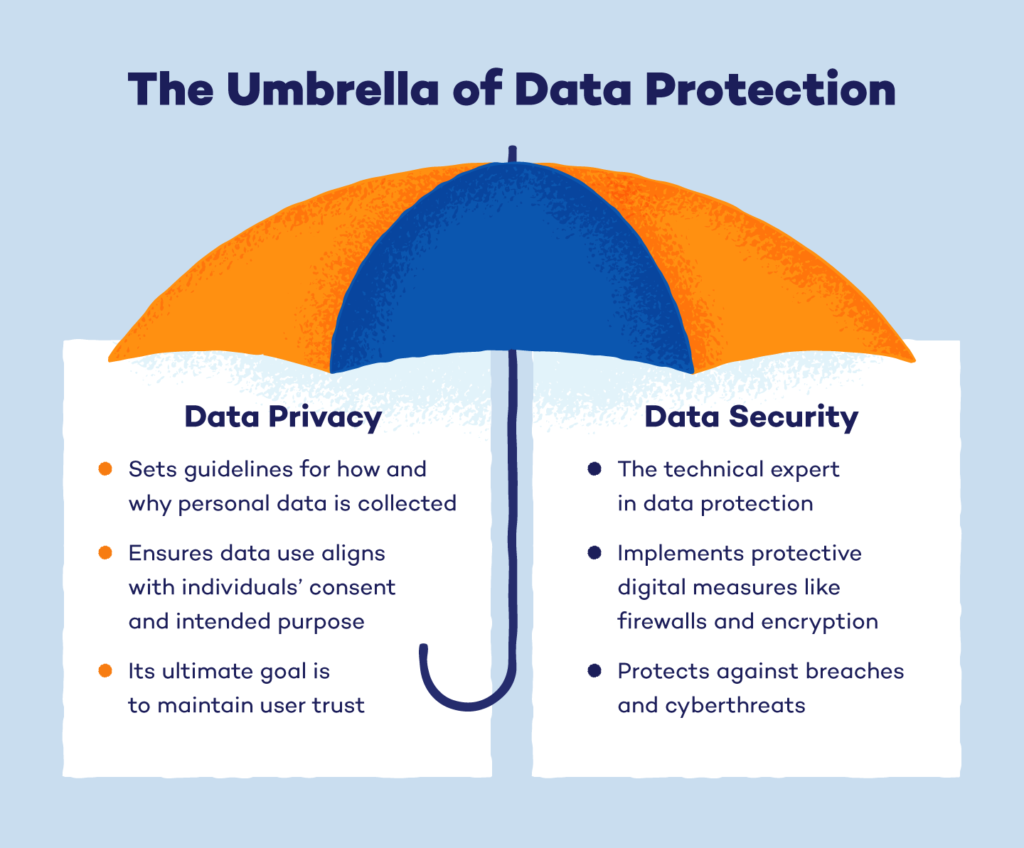
What is Data Privacy?
Data privacy, at its core, is about ensuring that personal and sensitive information is collected, stored, and processed securely, and only used for its intended purpose. For businesses, this means protecting the data of customers, employees, and stakeholders from unauthorised access and breaches.
The Importance of Data Privacy in Business
1) Protecting Customer Trust
Customers entrust businesses with their personal information, and safeguarding this data is crucial for maintaining their trust. Any breach or misuse of data can severely damage a company’s reputation and lead to a loss of customer confidence.
In a competitive market, trust is a key differentiator. Companies that prioritise data privacy can build stronger relationships with their customers, enhancing loyalty and long-term engagement.
2) Legal Compliance
Various regulations mandate businesses to implement stringent data protection measures. Failure to comply with these laws can result in hefty fines, legal penalties, and damage to the company’s reputation.
Regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States and APEC Privacy Framework in the Asia-Pacific region have set strict guidelines on how businesses should handle personal data.
3) Preventing Financial Loss
Data breaches can be extremely costly, not only in terms of financial penalties but also in lost business and remediation costs. Implementing robust data privacy measures helps mitigate the risk of breaches and their associated costs.
Beyond direct financial loss, businesses also face the indirect costs of reduced productivity and the resources needed to recover from a breach.
Key Compliance Regulations
Data privacy regulations vary significantly across the globe, with each region adopting frameworks that address their specific needs and concerns. Beyond the well-known GDPR in Europe and CCPA in the United States, the Asia-Pacific region and India have also developed robust data privacy regulations to protect personal information. Understanding these regulations is crucial for businesses operating in these markets.
1) General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
The GDPR is a comprehensive data protection law that applies to all businesses operating in the European Union (EU) or handling the data of EU citizens. It mandates strict guidelines on data collection, processing, and storage, with significant penalties for non-compliance.
Key provisions include obtaining explicit consent for data processing, ensuring data portability, and reporting breaches within 72 hours.
2) California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)
The CCPA grants California residents extensive rights over their personal data, including the right to know what data is being collected, the right to delete personal data, and the right to opt-out of the sale of their data.
Businesses must provide transparent information about their data practices and honour consumer requests regarding their data.
3) Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) Privacy Framework
The APEC Privacy Framework provides guidelines for data protection and privacy across the Asia-Pacific region, promoting a balance between information privacy protection and the free flow of information.
It encourages member economies to adopt a consistent approach to data privacy, facilitating cross-border data flows while ensuring adequate protection of personal information.
The framework includes principles such as preventing harm, notice, collection limitation, uses of personal information, choice, integrity, security safeguards, and access and correction.
Data & Privacy Laws in India
1) Information Technology (Reasonable Security Practices and Procedures and Sensitive Personal Data or Information) Rules, 2011
- These rules, under the Information Technology Act, 2000, set standards for the handling of sensitive personal data or information (SPDI) in India.
- They require businesses to implement reasonable security practices, obtain consent for data collection and sharing, and provide individuals with access to their data for correction and updating.
- Organisations must also adopt a privacy policy, ensure data protection through contractual obligations, and regularly audit their security practices.
2) The Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023
The Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023 (DPDPA) is a landmark legislation in India, focusing on the protection of personal data in the digital age. It sets stringent guidelines for the collection, storage and processing of personal data.
Here are some of its salient features and guidelines:
- Scope and Applicability: The DPDPA applies to the processing of personal data within India, including data of individuals residing in India and data processed by Indian entities outside the country.
- Consent and Data Processing: The Act mandates explicit consent from individuals before collecting or processing their personal data. Consent must be informed, clear, and specific, ensuring individuals understand how their data will be used.
- Data Protection Rights: Individuals are granted several rights over their personal data, including the right to access, correct, and delete their data, as well as the right to data portability and to be informed about data breaches.
- Data Fiduciaries and Data Processors: The Act defines the roles and responsibilities of data fiduciaries (entities that determine the purpose and means of data processing) and data processors (entities that process data on behalf of fiduciaries), emphasising accountability and transparency.
- Penalties for Non-Compliance: The DPDPA imposes significant penalties for non-compliance, including fines based on a percentage of global turnover, solidifying the importance of adhering to these regulations.
Effective Security Measures
1) Data Encryption
- Encrypting data ensures that even if it is intercepted or accessed without authorization, it cannot be read without the decryption key. This applies to both data at rest (stored data) and data in transit (data being transferred).
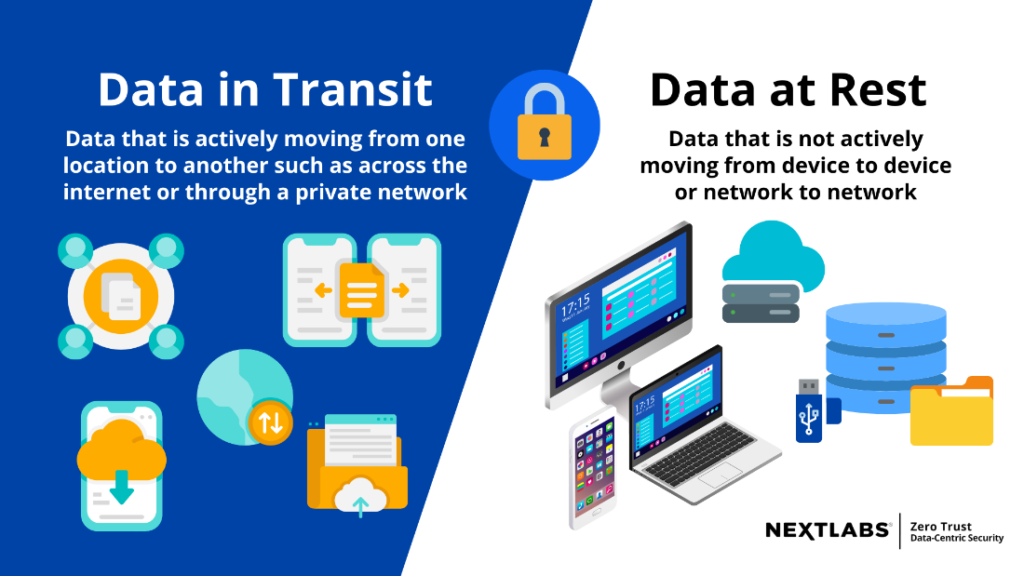
- Businesses should implement strong encryption protocols and regularly update them to guard against new threats.
2) Access Controls
- Implementing strict access controls ensures that only authorised personnel can access sensitive information. This can be achieved through user authentication, role-based access and multi-factor authentication (MFA).
- Regularly reviewing and updating access permissions helps prevent unauthorised access and potential breaches.
3) Regular Audits and Monitoring
- Conducting regular audits and continuous monitoring of data systems helps identify vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with data protection policies.
- Monitoring tools can detect unusual activity or potential security breaches in real-time, allowing for a swift response to mitigate risks.
4) Employee Training
- Employees are often the weakest link in data security. Regular training and awareness programs can help ensure that all staff understand the importance of data privacy and follow best practices to protect sensitive information.
- Training should cover recognising phishing attempts, proper data handling procedures and the importance of reporting suspicious activities.
5) Incident Response Plan
- Having a well-defined incident response plan in place ensures that businesses can respond quickly and effectively to data breaches or security incidents. This includes identifying the breach, containing the impact, notifying affected parties and taking corrective actions.
- Regularly testing and updating the incident response plan ensures preparedness for potential threats.
Bottom Line
Data privacy regulations in the Asia-Pacific region and India reflect a growing global consensus on the importance of protecting personal information. Businesses operating in these regions must adhere to complex regulatory laws, ensuring compliance with diverse data protection laws.
By understanding and following these regulations, companies can protect customer trust, avoid legal penalties and create a culture of data privacy and security.


